introduction to C
introduction and history of c
C is a middle-level procedure oriented programming language, used in general purpose programming, developed by Dennis Ritchie at AT&T Bell labs, USA between 1969 and 1973.
- “C” became popular because of its reliability, simple and easy to use.
- It was friendly, capable and reliable.
- ALGOL 60 was developed and did not become popular because it was too general and too abstract.
- They developed “CPU” (Combined Programming Language).
- It can be compiled on a variety of computer platforms.
- Next as it could not come up to make ALGOL 60 better one they moved to “BCPL” (Basic Combines Programming Language. Developed by martin Richard Cambridge University).
- . At the same time a language called “B” written by ken Thompson at AT & T‟S. Bell laboratories as a further simplification of BCPL.
C Programming Language Version History:
- 1972- Traditional C- Denis Richie
- 1978- K & R C - Kernighan and Richie
- 1989- ANSI C - ANSI Committee
- 1990- ANSI/ISO C - ISO Committee
- 1999- C 99 - Standardization Committee
Importance of C language:
- In 1988, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) has formalized the C language.
- C was invented to write UNIX operating system.
- UNIX is considered to be one of the most robust and secured operating system. C was used to write it, So C is very efficient that it can be used to create an OS.
- C is a successor of ‘Basic Combined Programming Language’ (BCPL) called B language.
- Linux OS, PHP and MySQL are written in C.
- C has been written in assembly language.
- C has high flexibility means a function can be written and can be used so many times at so many places. It increases the modularity.
- Rich set of library support.
- It can be compiled on a variety of computer platforms.
- The C language is used for developing system applications that forms a major portion of operating
systems such as Windows, UNIX and Linux. Below are some examples
where C language is being used:
- a) Database systems
- b) Graphics packages
- c) Word processors
- d) Spreadsheets
- e) Operating system development
- f) Compilers and Assemblers
character Set:
- A character represents any alphabet, digit, special character used to form words, numbers and expressions
- While space characters are ignored by ‘ C ’ compiler in cases where they are not part of a string constant.
- C character set can be divided into following groups :
- Alphabets : A……..Z to a……z.
- Digits : 0……….9.
- Special character : ~ , # ,$ , % ,^ ,* , & , + , -,\ , | , ( , ) etc.
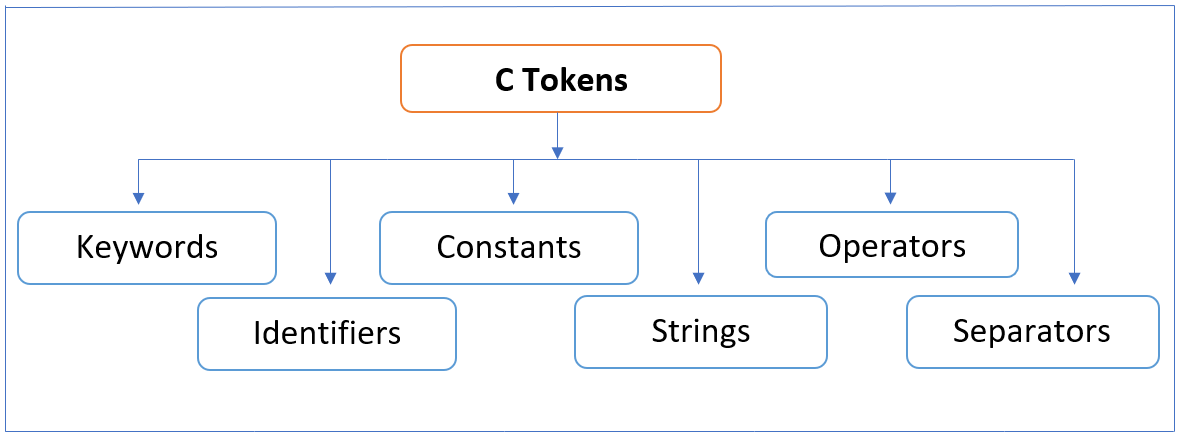
C Tokens or Lexical units:
Smallest individual units of a ‘c’ program are known as tokens.
C tokens are of following types. They are,
- Keywords: Example: int, continue, float etc.
- Identifiers: Example: main, total, printf etc.
- Constants: Example: 10, 20, 21.21 etc.
- Strings: Example: “sum”, “Amol” etc.
- Special symbols or separators: Example: (), {}, ; etc.
- Operators: Example: +, / ,- ,* etc.
void main()
{
int a,b,sum;
a=10; b=11;
sum=a+b;
printf (“Sum = %d \n”,sum);
getch();
}
Here in above code, a, b, sum, +, printf, main all are tokens also known as lexical units of a program
Keywords in C language:
- Keywords are nothing but pre-defined or reserved words in a C language.
- Each keyword is meant to perform a specific function in a C program.
- Since keywords are reserved words for compiler, they can’t be used as variable name.
- C language supports 32 keywords which are given below.
- C99 version adds 5 more keywords.
- Most of the keywords are assigned for Data Types, Storage Classes, Control Statements etc.
| Keywords in C Programming | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| auto | break | case | char |
| const | continue | default | do |
| double | else | enum | extern |
| float | for | goto | if |
| int | long | register | return |
| short | signed | sizeof | static |
| struct | switch | typedef | union |
| unsigned | void | volatile | while |
Identifiers in C language:
Names given to identify variables, functions, constants are called as identifiers.
Example: a, b, sum are a names given to integer variables are called identifiers in above example.
main, printf are the names given to function are called identifiers in above example.
Rules for constructing identifier name in C:
- First character should be an alphabet or underscore.
- Succeeding characters might be digits or letter.
- Punctuation and special characters are not allowed except underscore.
- Identifiers should not be keywords.
C Constants:
These are also like normal variables. But, only difference is, their values cannot be modified by the program once they are defined.
- Constants refer to fixed values. They are also called as literals.
- Constants may be belonging to any of the data type.
- Syntax:
- const data_type variable_name; // In ANSI C language
- #define Constant_name value // In traditional C language
Structure of C programming:
| Documentation section |
|---|
| Header files section |
| Symbolic constants section |
| Global variables declaration |
| Function declaration or prototype |
| // main function section return_type main() { Variable declaration or initialization Executable statements } |
| //user-defined function return_type Function_name (list of arguments) { Body of function } |
Data types in C
- • C data types are defined as the data storage format that a variable can store a data to perform a specific operation.
- • Data types are used to define a variable before to use in a program.
- • Size of variable, constant and array are determined by data types.
- • Static memory management is function of compiler so compiler must know how many bytes are reserved for particular data type and which type of value we should store in that particular data type. That information about variable is given by data type to compiler.
- • On other hand storage classes gives the information about on which memory partition we have to store variable value to the compiler.
- • Memory allocation for variable is done by compiler and for that purpose compiler must know how many bytes are required to store that variable and that information is given by data type. And where to store that variable on RAM because RAM having four logical partitions that is stack, heap, static or global partition is given by storage class to compiler.
Syntax
[Storage class] <Data Type> Name_of_variable ;
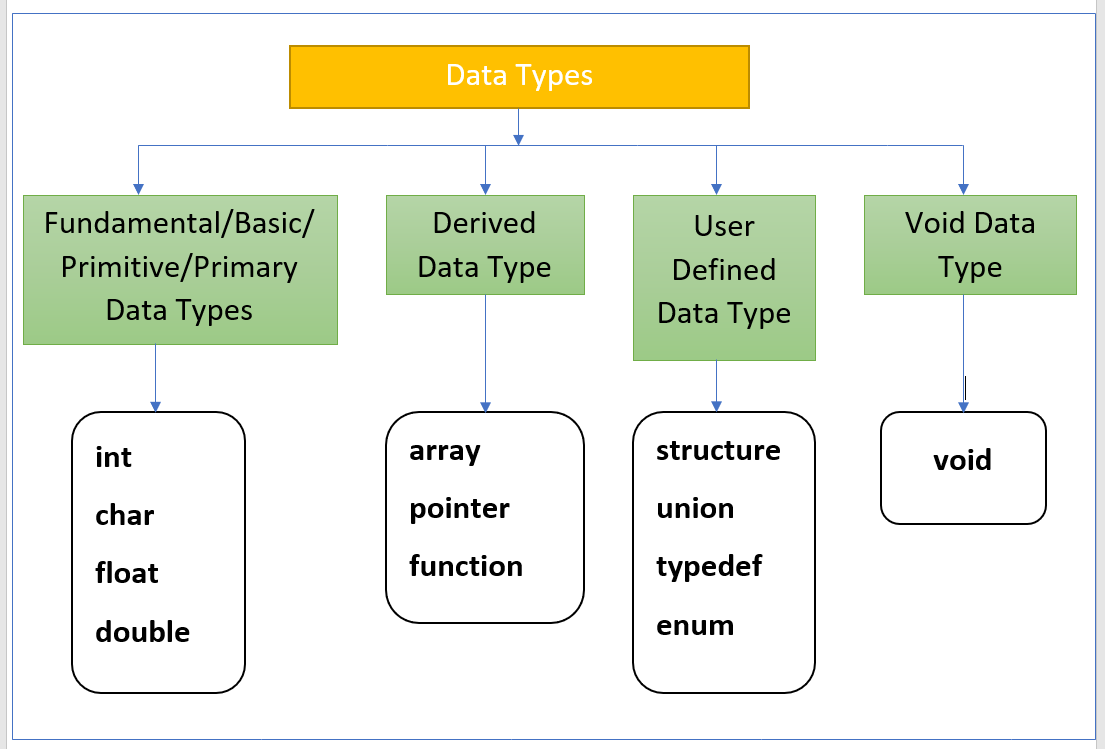
Fundamental/Basic/Primitive/Primary data types in C:
1.integer data type:
- Integer data type allows a variable to store numeric values.
- “int” keyword is used to refer integer data type.
- The storage size of int data type is 2 or 4 or 8 byte.
- It varies depend upon the processor in the CPU that we use. If we are using 16 bit processor, 2 byte (16 bit) of memory will be allocated for int data type.
- Like wise, 4 byte (32 bit) of memory for 32 bit processor and 8 byte (64 bit) of memory for 64 bit processor is allocated for int datatype.
- Depends on version if traditional C language int data type’s size is 2 bytes and in ANSI C int data type requires 4 bytes.
- int (4 byte) can store values from -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.
- int (2 byte) can store values from -32,768 to +32,767.
2.Character data type:
- Character data type allows a variable to store only one character.
- Storage size of character data type is 1. We can store only one character using character data type.
- “char” keyword is used to refer character data type.
- For example, ‘S’ can be stored using char data type. You can’t store more than one character using char data type.
3 Floating point data type:
Floating point data type consists of 2 types. They are,
- float- Storage size of float data type is 4. This also varies depend upon the processor in the CPU as “int” data type.
- double-•Double data type is also same as float data type which allows up-to 10 digits after decimal. The range for double data type is from 1E–37 to 1E+37.
Derived data types in C:
A derived types are inherited from fundamental or user defined data types like int, float, structure etc. Using derived types, an infinite variety of new types can be formed. Examples: Array, pointer, function etc.
A pointer is a variable which stores the address of another variable. Array is a collection of similar data elements.
User defined Data types in C:
Sometimes, a basic set of data types defined in C language are insufficient for our application. Programmer can create their own data types as per application needs are called as user defined data types.
Examples: Structure, union, enum, typedef etc.
void data type in C:
Void is an empty data type that has no value.
This can be used as return type of functions and void
pointers means generic pointers.
Modifiers in C:
- The amount of memory space to be allocated for a variable by data type is modified by modifiers.
- Modifiers are prefixed with basic data types to modify (either increase or decrease) the amount of storage space allocated to a variable.
- For example, storage space for int data type is 4 byte for 32 bit processor. We can increase the range by using long int which is 8 byte. We can decrease the range by using short int which is 2 byte.
- There are 5 modifiers available in C language. They are,
- short
- long
- signed
- unsigned
Signed means that variable can take both positive and negative values and unsigned means only the positive
values. Int means data type is by default signed int and unsigned int data type is unsigned int. Last bit in
the int data type is reserved for sign, if last bit is 0 then that is positive number and if last bit
contains 1 then that is negative number.
Below table gives the detail about the storage size of each C basic data type in 16 bit processor.
Please keep in mind that storage size and range for int and float data type will vary depend on the CPU
processor and versions of C (8, 16, 32 and 64 bit).